v6
React Router v6 정식 릴리즈
2021년 11월 4일 v6.0.0 beta → release 출시되었습니다.
React v16.8 이상으로 업그레이드
단, React ≥ 15 이상이면 react router v5 이상을 호환하고 있어서 v6로 업그레이드 하지 않더라도 react만 업그레이드 가능합니다.
React Router v6 장점
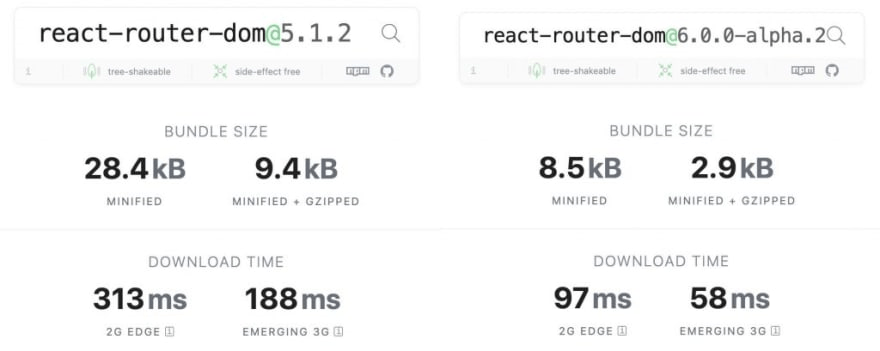
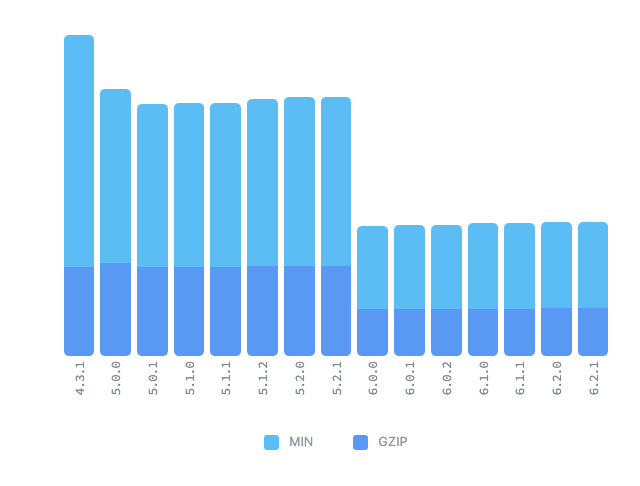
- 기존 버전에 비해서 버들 사이즈가 70% 정도 감소했습니다.(빌드시간 감소??)
v5.1 버전의 크기는 9.4kb → v6 버전의 크기는 2.9kb로 감소했습니다.
- React Hooks 전반적인 지원(hoc 등 기능지원 들이 사라짐)
- 구 브라우저에 대한 지원 중단(단, polyfill 사용으로 대응가능)
- IE 11 지원
- package.json IE11 브라우저 지원하도록 추가
"browserslist": { "production": [ "...", "ie 11" ], "development": [ "...", "ie 11" ] },- polyfill 추가
- react-app-polyfill(facebook 제공)
- 리액트 개발에서 사용하는 다양한 문법을 변환해주는 라이브러리
- Promise, window.fetch, Symbol, Object.assign, Array.from + [ IE9 Map, Set ]와 같은 필요한 것만 포함하고 있어 사이즈가 작아 가벼운 게 특징
// src/index.tsx // 첫번째 라인에 추가 import 'react-app-polyfill/ie11'; import 'react-app-polyfill/stable'; // async,await,generator 문법사용 import React from 'react'; - react-app-polyfill(facebook 제공)
- IE 11 지원
- 상대경로 사용으로 인한 코드량 감소(match.url, match.path)
- 기능에 대한 단일화된 표준
- 예) Router → element 통합
React Router v6 설치
npm install react-router-dom // react-router-dom@6Switch → Routes 변경사항
- Switch 처럼 순서를 기준으로 선택하는 것이 아닌, 가장 일치하는 라우트를 기반인 기능으로 변경
- Switch → Routes 변경(route는 routes에 children이어야 함)
- exact props 삭제
- 서브경로가 필요한 경우 path * 사용
- component, children, render → element 통일
// v6 이전
<Switch>
<Route path="/about" render={() => <About />} />
<Route exact path="/" component={Home} />
<Route path={'/*'}> // <Route>
<div>Not Found</div>
</Route>
</Switch>
// v6 이후
<Routes>
<Route path="/about" element={<About />} />
<Route path="/" element={<Home />} />
<Route path={'/*'} element={<div>Not Found</div>} />
</Routes>withRouter → hooks 변경사항
- withRouter 삭제로 인한 hooks api 변경
- match: useMatch → 현재 상대경로(단, 속성값이 달라져서 확인필요)
- history: useNavigate 지원
- location: useLocation ( v5 이후에서도 지원)
// v6 이전
import React from 'react';
import { RouteComponentProps } from 'react-router';
import { withRouter } from 'react-router-dom';
interface MatchParams {
id: string;
}
const WithRouter = ({
match,
location,
history,
}: RouteComponentProps<MatchParams>) => {
return (
<>
<h1>WithRouter</h1>
<p>{match?.params?.id}</p>
<p>{location.pathname}</p>
<p>{history.length}</p>
</>
);
};
WithRouter.defaultProps = {};
export default withRouter(WithRouter);
// v6 이후
import React from 'react';
import { useMatch, useNavigate, useLocation } from 'react-router-dom';
const WithRouter = () => {
const match = useMatch('/with/:id');
const history = useNavigate();
const location = useLocation();
return (
<>
<h1>WithRouter</h1>
<p>{match?.params?.id}</p>
<p>{location.pathname}</p>
<p>{history.length}</p>
</>
);
};
WithRouter.defaultProps = {};
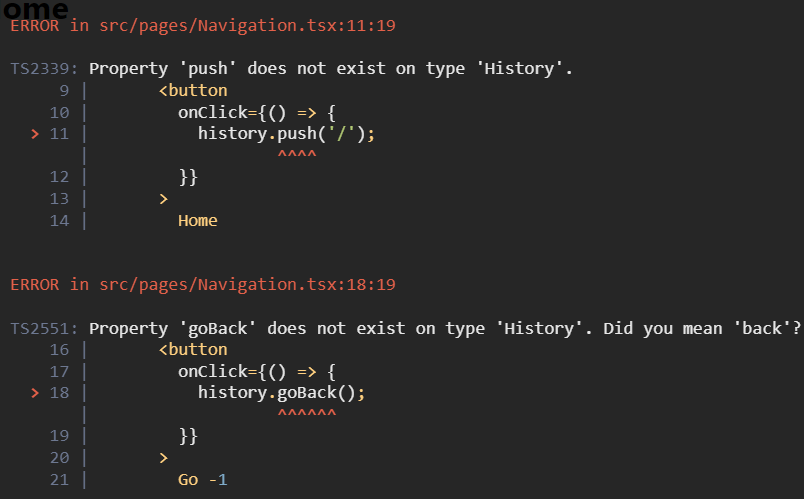
export default WithRouter;useHistory → useNavigate 변경사항
useHistory hooks 대체로 useNavigate 변경
- useHistory 리턴값(객체) vs useNavigate 리턴값(함수)
- 기존에는 용도에 맞게 go, goBback, goForward, push, replace 메서드 호출에서 직관적인 함수호출로 변경
// v6 이전
import React from 'react';
import { useHistory } from 'react-router';
const Navigation = () => {
const history = useHistory();
return (
<div>
<button
onClick={() => {
history.push('/');
}}
>
Home
</button>
<button
onClick={() => {
history.goBack();
}}
>
Go -1
</button>
<button
onClick={() => {
history.go(-2);
}}
>
Go -2
</button>
<button
onClick={() => {
history.push('/about');
}}
>
Go to about
</button>
<button
onClick={() => {
history.replace('Item/2');
}}
>
Replace to Item
</button>
</div>
);
};
Navigation.defaultProps = {};
export default Navigation;
// v6 이후
import React from 'react';
import { useNavigate } from 'react-router';
const Navigation = () => {
const navigation = useNavigate();
return (
<div>
<button
onClick={() => {
navigation('/'); // vs history.push('/');
}}
>
Home
</button>
<button
onClick={() => {
navigation(-1); // vs history.goBack();
}}
>
Go -1
</button>
<button
onClick={() => {
navigation(-2); // vs history.go(-2);
}}
>
Go -2
</button>
<button
onClick={() => {
navigation('/about'); // vs history.push('/about');
}}
>
Go to about
</button>
<button
onClick={() => {
navigation('Item/2', {
// vs history.replace('Item/2');
replace: true,
});
}}
>
Replace to Item
</button>
</div>
);
};
Navigation.defaultProps = {};
export default Navigation;useRouteMatch 변경사항
- useRouteMatch 사라져서, 기존에 현재 url을 얻기위한 match.path, match.url 사라짐
- 현재 라우터 기준의 상대경로로 변경
// v6 이전
import React from 'react';
import { Link, Route, useParams, useRouteMatch } from 'react-router-dom';
import About from './About';
import Main from './Main';
type UserProps = {
id: string;
};
const User = () => {
const match = useRouteMatch();
const { id } = useParams<UserProps>();
return (
<>
<h1>{`User ${id}`}</h1>
<ul>
<li>
<Link to={`${match.url}`}>Main</Link>
</li>
<li>
<Link to={`${match.url}/about`}>About</Link>
</li>
</ul>
<Route path={match.path} exact>
<Main />
</Route>
<Route path={`${match.path}/about`} exact>
<About />
</Route>
</>
);
};
User.defaultProps = {};
export default User;
// v6 이후
// user 서브 경로 추가하기 위해서 * 추가
function App() {
return (
<>
<Navigation />
<Routes>
<Route path="/about" element={<About />} />
<Route path="/users/:id/*" element={<User />} />
<Route path="/with/:id" element={<WithRouter />} />
<Route path="/" element={<Home />} />
<Route path={'*'} element={<div>Not Found</div>} />
</Routes>
</>
);
}
import React from 'react';
import { Link, Route, Routes, useParams } from 'react-router-dom';
import About from './About';
import Main from './Main';
type UserProps = {
id: string;
};
const User = () => {
// const match = useRouteMatch();
const { id } = useParams<UserProps>();
return (
<>
<h1>{`User ${id}`}</h1>
<ul>
<li>
<Link to="">Main</Link>
</li>
<li>
<Link to="about">About</Link>
</li>
</ul>
<Routes>
<Route path="" element={<Main />} />
<Route path="about" element={<About />} />
</Routes>
</>
);
};
User.defaultProps = {};
export default User;서브라우터에 다른 구현 Outlet
// v6 이전
// App.tsx
<Route path="/user/:id">
<User />
</Route>
// User.tsx
<>
<h1>{`User ${id}`}</h1>
<ul>
<li>
<Link to={`${match.url}`}>Main</Link>
</li>
<li>
<Link to={`${match.url}/about`}>About</Link>
</li>
</ul>
<Route path={match.path} exact>
<UserMain />
</Route>
<Route path={`${match.path}/about`} exact>
<UserAbout />
</Route>
</>
// v6 이후
// App.tsx
<Route path="/useroutlet/:id/*" element={<UserOutlet />}>
<Route path="" element={<UserMain />} />
<Route path="about" element={<UserAbout />} />
</Route>
// User.tsx
<>
<h1>{`User ${id}`}</h1>
<ul>
<li>
<Link to="">Main</Link>
</li>
<li>
<Link to="about">About</Link>
</li>
</ul>
<Outlet />
</>Optional URL → Multi Route 추가
// v6 이전
<Route path="/optional/:value?" element={<Optional />} />
// v6 이후
<Route path="/optional/:value" element={<Optional />} />
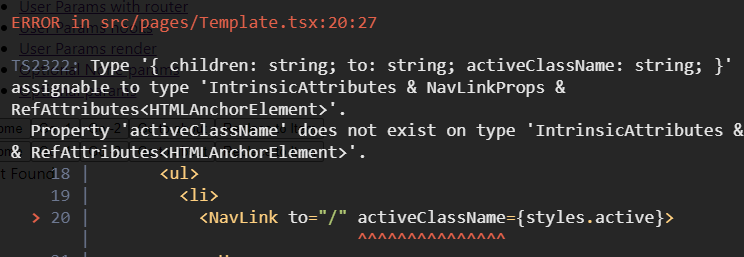
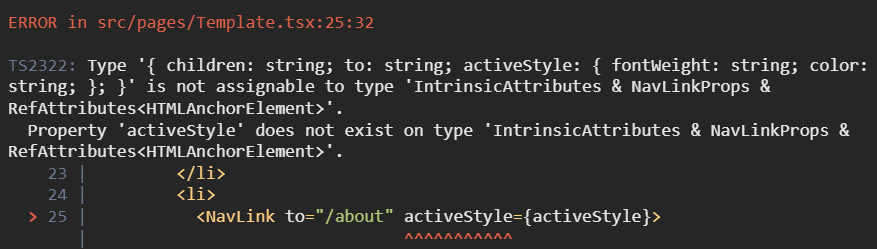
<Route path="/optional/" element={<Optional />} />NavLink 변경사항
-
activeStye, activeClassName 사라지고, isActive Props로 변경
- activeClassName → className={({ isActive }) => (isActive ? styles.active : ”)}
- activeStyle={activeStyle} → style={({ isActive }) => (isActive ? activeStyle : {})}
-
exact → end 로 변경
// v6 이전 import React from 'react'; import { NavLink } from 'react-router-dom'; import styles from './Template.module.scss'; import Navigation from './Navigation'; type TemplateProps = { children: React.ReactChild; }; const Template = ({ children }: TemplateProps) => { const activeStyle = { fontWeight: 'bold', color: 'red', }; return ( <div> <ul> <li> <NavLink to="/" exact activeClassName={styles.active}> Home </NavLink> </li> <li> <NavLink to="/about" activeStyle={activeStyle}> About </NavLink> </li> <li> <NavLink to="/with/1" activeStyle={activeStyle}> User Params with router </NavLink> </li> <li> <NavLink to="/user/1" activeStyle={activeStyle}> User Params hooks </NavLink> </li> <li> <NavLink to="/item/2" activeStyle={activeStyle}> User Params render </NavLink> </li> <li> <NavLink to="/optional" exact activeStyle={activeStyle}> Optional None params </NavLink> </li> <li> <NavLink to="/optional/3" activeStyle={activeStyle}> Optional params </NavLink> </li> </ul> <Navigation /> {children} </div> ); }; Template.defaultProps = {}; export default Template; // v6 이후 import React from 'react'; import { NavLink } from 'react-router-dom'; import styles from './Template.module.scss'; import Navigation from './Navigation'; type TemplateProps = { children: React.ReactChild; }; const Template = ({ children }: TemplateProps) => { const activeStyle = { fontWeight: 'bold', color: 'red', }; return ( <div> <ul> <li> <NavLink to="/" className={({ isActive }) => (isActive ? styles.active : '')} > Home </NavLink> </li> <li> <NavLink to="/about" style={({ isActive }) => (isActive ? activeStyle : {})} > About </NavLink> </li> <li> <NavLink to="/with/1" style={({ isActive }) => (isActive ? activeStyle : {})} > User Params with router </NavLink> </li> <li> <NavLink to="/user/1" style={({ isActive }) => (isActive ? activeStyle : {})} > User Params hooks </NavLink> </li> <li> <NavLink to="/useroutlet/1" style={({ isActive }) => (isActive ? activeStyle : {})} > User Outlet Params hooks </NavLink> </li> <li> <NavLink to="/item/2" style={({ isActive }) => (isActive ? activeStyle : {})} > User Params render </NavLink> </li> <li> <NavLink to="/optional" end style={({ isActive }) => (isActive ? activeStyle : {})} > Optional None params </NavLink> </li> <li> <NavLink to="/optional/3" style={({ isActive }) => (isActive ? activeStyle : {})} > Optional params </NavLink> </li> </ul> <Navigation /> {children} </div> ); }; Template.defaultProps = {}; export default Template;
Redirect → Navigate 변경사항
// v6 이전
<Switch>
<Redirect path="/main" to="/user/1" />
</Switch>
// v6 이후
<Routes>
<Route path="/main" element={<Navigate replace to="/user/1" />} />
</Routes>renderRoutes → useRoutes
기존의 react-router-config의 renderRouters가 useRoutes라는 Hook 으로 변경됨.
// v6 이전
// react-router-config
// yarn add react-router-config로 설치 후 사용
import { renderRoutes } from 'react-router-config';
const routes = [
{
component: Root,
routes: [
{
path: '/',
exact: true,
component: Home,
},
{
path: '/child/:id',
component: Child,
routes: [
{
path: '/child/:id/grand-child',
component: GrandChild,
},
],
},
],
},
];
const Root = ({ route }) => (
<div>
<h1>Root</h1>
{/* 자식 라우트들이 렌더할 수 있도록 renderRoutes 실행 */}
{renderRoutes(route.routes)}
</div>
);
const Home = ({ route }) => (
<div>
<h2>Home</h2>
</div>
);
const Child = ({ route }) => (
<div>
<h2>Child</h2>
{/* renderRoutes가 없으면 자식들은 렌더되지 않음 */}
{renderRoutes(route.routes)}
</div>
);
const GrandChild = ({ someProp }) => (
<div>
<h3>Grand Child</h3>
<div>{someProp}</div>
</div>
);
ReactDOM.render(
<BrowserRouter>
{/* renderRoutes에 가장 처음 정의했던 routes 자체를 뿌려줌으로써 차례로 렌더링될 수 있도록 함 */}
{renderRoutes(routes)}
</BrowserRouter>,
document.getElementById('root'),
);
// v6 이후
function App() {
const element = useRoutes([
// Route에서 사용하는 props의 요소들과 동일
{ path: '/', element: <Home /> },
{ path: 'dashboard', element: <Dashboard /> },
{
path: 'invoices',
element: <Invoices />,
// 중첩 라우트의 경우도 Route에서와 같이 children이라는 property를 사용
children: [
{ path: ':id', element: <Invoice /> },
{ path: 'sent', element: <SentInvoices /> },
],
},
// NotFound 페이지는 다음과 같이 구현할 수 있음
{ path: '*', element: <NotFound /> },
]);
// element를 return함으로써 적절한 계층으로 구성된 element가 렌더링 될 수 있도록 함
return element;
}Migrating to RouterProvider(with createBrowserRouter)
도입배경
createBrowserRouter가 도입된 이유와 장점입니다:
- 단순화된 라우팅 설정: createBrowserRouter를 사용하면 라우트 구성을 하나의 객체로 선언할 수 있습니다. 이로 인해 라우트 설정을 보다 간단하고 일관성 있게 관리할 수 있습니다.
- 라우트 데이터 로딩: createBrowserRouter는 데이터 로딩을 더 쉽게 처리할 수 있는 기능을 제공합니다. 라우트마다 데이터를 로드하고, 이를 loader 함수를 통해 처리할 수 있습니다. 이로 인해 데이터와 라우트 설정을 한 곳에서 관리할 수 있습니다.
- 중첩 라우트의 간편한 관리: 중첩 라우트(nested routes)를 설정하는 것도 더 직관적입니다. createBrowserRouter는 중첩 라우트를 선언적이고 명확하게 관리할 수 있는 구조를 제공합니다.
- 에러 경계(Error Boundaries): 각 라우트에 에러 경계를 쉽게 추가할 수 있습니다. createBrowserRouter를 사용하면 특정 라우트에서 발생하는 오류를 처리하기 위해 에러 경계를 설정하는 것이 간편해집니다.
- 경량화 및 최적화: React Router v6는 성능과 사용성을 고려하여 많은 부분이 최적화되었습니다. createBrowserRouter는 이러한 최신 최적화를 활용할 수 있는 구조를 제공합니다.
client side routing
import * as React from 'react';
import { createRoot } from 'react-dom/client';
import {
createBrowserRouter,
RouterProvider,
Route,
Link,
} from 'react-router-dom';
// v5 이전
// router components
<BrowserRouter>
<Switch>
<Route
path="/"
component={
<div>
<h1>Hello World</h1>
<Link to="about">About Us</Link>
</div>
}
/>
<Route exact path="/about" component={<div>About</div>} />
</Switch>
</BrowserRouter>;
// v6
// client routers
const router = createBrowserRouter([
{
path: '/',
element: (
<div>
<h1>Hello World</h1>
<Link to="about">About Us</Link>
</div>
),
},
{
path: 'about',
element: <div>About</div>,
},
]);
createRoot(document.getElementById('root')).render(
<RouterProvider router={router} />,
);Nested Routes
path 지정 시에 상대경로를 지정해줄 수 있게 되면서 중첩 라우팅 구현이 가능하며, 자식 패스는 부모 패스의 상대 경로로 설정됩니다.
- createRoutesFromElements(Configure nested routes with JSX)
// Configure nested routes with JSX createBrowserRouter( createRoutesFromElements( <Route path="/" element={<Root />}> <Route path="contact" element={<Contact />} /> <Route path="dashboard" element={<Dashboard />} loader={({ request }) => fetch('/api/dashboard.json', { signal: request.signal, }) } /> <Route element={<AuthLayout />}> <Route path="login" element={<Login />} loader={redirectIfUser} /> <Route path="logout" action={logoutUser} /> </Route> </Route>, ), ); - use plain objects
createBrowserRouter([ { path: '/', element: <Root />, children: [ { path: 'contact', element: <Contact />, }, { path: 'dashboard', element: <Dashboard />, loader: ({ request }) => fetch('/api/dashboard.json', { signal: request.signal, }), }, { element: <AuthLayout />, children: [ { path: 'login', element: <Login />, loader: redirectIfUser, }, { path: 'logout', action: logoutUser, }, ], }, ], }, ]);
dynamicsegments
<Route path="projects/:projectId/tasks/:taskId" />
// If the current location is /projects/abc/tasks/3
<Route
// sent to loaders
loader={({ params }) => {
params.projectId; // abc
params.taskId; // 3
}}
// and actions
action={({ params }) => {
params.projectId; // abc
params.taskId; // 3
}}
element={<Task />}
/>;
function Task() {
// returned from `useParams`
const params = useParams();
params.projectId; // abc
params.taskId; // 3
}
function Random() {
const match = useMatch(
"/projects/:projectId/tasks/:taskId"
);
match.params.projectId; // abc
match.params.taskId; // 3
}ranked routematching
teams/new 링크 이동 시 2개 라우터가 같이 매칭되지만 랭킹 알고리즘에 의해서 /teams/new 라우터로 연결됩니다.
<Route path="/teams/:teamId" />
<Route path="/teams/new" />active links
// isActive: user knows where they are (isActive)
// isPending: where they're going (isPending)
<NavLink
style={({ isActive, isPending }) => {
return {
color: isActive ? 'red' : 'inherit',
};
}}
className={({ isActive, isPending }) => {
return isActive ? 'active' : isPending ? 'pending' : '';
}}
/>;
function SomeComp() {
const match = useMatch('/messages');
return <li className={Boolean(match) ? 'active' : ''} />;
}relative links
<Route path="home" element={<Home />}>
<Route path="project/:projectId" element={<Project />}>
<Route path=":taskId" element={<Task />} />
</Route>
</Route>In <Project> @ /home/project/123 |
Resolved <a href> |
|---|---|
<Link to="abc"> |
/home/project/123/abc |
<Link to="."> |
/home/project/123 |
<Link to=".."> |
/home |
<Link to=".." relative="path"> |
/home/project |
data loading
navigation 동안에 데이터의 로딩을 loader를 통해서 제공하고 있습니다.
또한, loader를 통해서 리턴한 값을 각 element에서는 useLoaderData를 통해서 얻어 올 수 있습니다.
// loader
<Route
path="/"
loader={async ({ request }) => {
// loaders can be async functions
const res = await fetch('/api/user.json', {
signal: request.signal,
});
const user = await res.json();
return user;
}}
element={<Root />}
>
<Route
path=":teamId"
// loaders understand Fetch Responses and will automatically
// unwrap the res.json(), so you can simply return a fetch
loader={({ params }) => {
return fetch(`/api/teams/${params.teamId}`);
}}
element={<Team />}
>
<Route
path=":gameId"
loader={({ params }) => {
// of course you can use any data store
return fakeSdk.getTeam(params.gameId);
}}
element={<Game />}
/>
</Route>
</Route>;
// useLoaderData
function Root() {
const user = useLoaderData();
// data from <Route path="/">
}
function Team() {
const team = useLoaderData();
// data from <Route path=":teamId">
}
function Game() {
const game = useLoaderData();
// data from <Route path=":gameId">
}redirects
데이터를 로딩/변경되는 동안 라우팅을 변경할 경우 redirect 메서드를 사용해서 이동이 가능합니다.
<Route
path="dashboard"
loader={async () => {
const user = await fake.getUser();
if (!user) {
// if you know you can't render the route, you can
// throw a redirect to stop executing code here,
// sending the user to a new route
throw redirect("/login");
}
// otherwise continue
const stats = await fake.getDashboardStats();
return { user, stats };
}}
/>
<Route
path="project/new"
action={async ({ request }) => {
const data = await request.formData();
const newProject = await createProject(data);
// it's common to redirect after actions complete,
// sending the user to the new record
return redirect(`/projects/${newProject.id}`);
}}
/>
pending navigation ui
다음 페이지를 렌더링 하기 전에 펜딩 UI를 표기하기 위해서 navigation.state를 사용하면 됩니다.
function Root() {
const navigation = useNavigation();
return (
<div>
{navigation.state === 'loading' && <GlobalSpinner />}
<FakeSidebar />
<Outlet />
<FakeFooter />
</div>
);
}skeleton-ui-with-suspense
페이지 이동 시 데이터를 얻어오는 중간에 defer 메서드를 사용 시 Suspense, Await 메서드 사용해서 로딩/스켈레톤 UI 사용이 가능합니다.
<Route
path="issue/:issueId"
element={<Issue />}
loader={async ({ params }) => {
// these are promises, but *not* awaited
const comments = fake.getIssueComments(params.issueId);
const history = fake.getIssueHistory(params.issueId);
// the issue, however, *is* awaited
const issue = await fake.getIssue(params.issueId);
// defer enables suspense for the un-awaited promises
return defer({ issue, comments, history });
}}
/>;
function Issue() {
const { issue, history, comments } = useLoaderData();
return (
<div>
<IssueDescription issue={issue} />
{/* Suspense provides the placeholder fallback */}
<Suspense fallback={<IssueHistorySkeleton />}>
{/* Await manages the deferred data (promise) */}
<Await resolve={history}>
{/* this calls back when the data is resolved */}
{resolvedHistory => <IssueHistory history={resolvedHistory} />}
</Await>
</Suspense>
<Suspense fallback={<IssueCommentsSkeleton />}>
<Await resolve={comments}>
{/* ... or you can use hooks to access the data */}
<IssueComments />
</Await>
</Suspense>
</div>
);
}
function IssueComments() {
const comments = useAsyncValue();
return <div>{/* ... */}</div>;
}form data mutations
form action을 사용해서 form 안에 데이터(name)를 얻어올 수 있습니다.
<Form action="/project/new">
<label>
Project title
<br />
<input type="text" name="title" />
</label>
<label>
Target Finish Date
<br />
<input type="date" name="due" />
</label>
</Form>
<Route
path="project/new"
action={async ({ request }) => {
const formData = await request.formData();
const newProject = await createProject({
title: formData.get("title"),
due: formData.get("due"),
});
return redirect(`/projects/${newProject.id}`);
}}
/>error-handling
에러가 생길 경우 errorElement 선언된 컴포넌트 렌더링이 가능합니다.
또한 자식 라우트에서 errorElement가 없는경우 부모 errorElement 따라가게 됩니다.
<Route
path="/"
loader={() => {
something.that.throws.an.error();
}}
// this will not be rendered
element={<HappyPath />}
// but this will instead
errorElement={<ErrorBoundary />}
/>
<Route
path="/"
element={<HappyPath />}
errorElement={<ErrorBoundary />}
>
{/* Errors here bubble up to the parent route */}
<Route path="login" element={<Login />} />
</Route>opts.basename
BaseURL 설정을 해야하는 경우 createBrowserRouter 2번쨰 인자에 옵션으로 설정이 가능합니다.
단, createBrowserRouter 선언 컴포넌트에서 동적 param을 basename으로 설정을 해야하는 경우 window.location.pathname을 통해서 동적 param을 얻어와서 정적 baseURL을 얻어올 수 있습니다.
createBrowserRouter(routes, {
basename: '/teams',
});
// /teams/:teamId
export const getBaseURLInfo = () => {
const pathname = window.location.pathname;
const prefix = '/teams';
const params = pathname
.replace(prefix, '')
.split('/')
.filter(param => param.length > 0);
if (params.length > 0) {
return {
baseName: `${prefix}/${params[0]}`,
baseParam: params[0],
};
}
return {
baseName: `${prefix}/${params[0]}`,
baseParam: '',
};
};Prompt 재구현(useBlocker)
function ImportantForm() {
let [value, setValue] = React.useState('');
// Block navigating elsewhere when data has been entered into the input
let blocker = useBlocker(
({ currentLocation, nextLocation }) =>
value !== '' && currentLocation.pathname !== nextLocation.pathname,
);
return (
<Form method="post">
<label>
Enter some important data:
<input
name="data"
value={value}
onChange={e => setValue(e.target.value)}
/>
</label>
<button type="submit">Save</button>
{blocker.state === 'blocked' ? (
<div>
<p>Are you sure you want to leave?</p>
<button onClick={() => blocker.proceed()}>Proceed</button>
<button onClick={() => blocker.reset()}>Cancel</button>
</div>
) : null}
</Form>
);
}Outlet, useOutletContext
패스별로 자식 컴포넌트를 선언을 다르게 해야할 경우 location pathname 분기 후 outlet을 처리를 진행할 수 있습니다.
또한 자식 컴포넌트에 데이터를 넘길 경우 context props 넘기고 자식 라우터 컴포넌트는 useOutletContext에서 값을 얻어올 수 있습니다.
{
location.pathname.indexOf('/a') > -1 ? (
<Outlet context={{ type: 'a' }} />
) : (
<Outlet context={{ type: 'b' }} />
);
}
export const B = () => {
const { type } = useOutletContext<{ type: string }>();
};